Packaging plays a pivotal role in any business involved in storing or transporting goods. A well-designed packaging solution safeguards products from damage, ensures quality, and streamlines logistical operations. For many businesses, the decision often comes down to choosing between expendable packaging (single-use) and returnable packaging—two distinct approaches that cater to different operational needs.
This article explores the differences between these packaging strategies, highlighting their unique applications, benefits, and challenges. We’ll discuss important factors, such as cost-effectiveness and sustainability, which can guide you toward a smarter packaging decision. With the expertise of Universal Package, a trusted provider of industrial packaging and material handling solutions, you’ll gain valuable insight into which option best aligns with your goals.
Key Differences Between Expendable and Returnable Packaging
The core distinction between expendable and returnable packaging lies in their intended usage and lifespan. Expendable packaging—such as corrugated cardboard boxes and foam padding—is typically designed for single use before disposal or recycling. Returnable packaging, by contrast, is robust enough for repeated cycles, making it well-suited to longer-term or repetitive shipping operations.
Functional Distinctions
Expendable solutions are lightweight and convenient for short-term or one-way shipments where retrieval is impractical. Returnable models, however, work best within established or closed-loop supply chains, offering durability over months or years.
Material Durability and Lifecycle
Expendable options often employ lightweight materials like cardboard, paperboard, or simple foam inserts. These are cost-efficient but degrade over time and require regular replacement. By comparison, returnable packaging commonly consists of stronger materials, such as plastics or metal components, which last longer and reduce overall waste.
Cost Considerations
Due to their lower initial expense, expendable solutions can be appealing for limited or one-off shipments. But for businesses that frequently transport goods, the cost of purchasing single-use packaging adds up quickly. Returnable packaging can entail higher upfront costs, yet the investment is recouped through multiple uses and reduced waste, particularly for predictable, recurring shipments.
Benefits and Use Cases of Expendable Packaging
Although not designed for repeated use, expendable packaging remains a practical choice in many contexts. It accommodates short-term or occasional shipping needs and often provides flexible, industry-specific options.
Ideal Applications
- Temporary or one-way shipments: Organizations that ship goods to distant locations, or those without viable reverse logistics, benefit from single-use packaging.
- Time-sensitive deliveries: When speed is critical, a disposable approach avoids any delay involved in container returns.
Lower Upfront Investment
Expendable materials have a lower purchase cost, making them suitable for businesses with tighter budgets or infrequent shipping schedules. Foam inserts or other specialized cushioning may also be customized quickly to protect fragile products without necessitating a long-term investment in containers or racks.
Custom Solutions for Specific Items
Industries requiring specialized, product-specific protection—such as delicate electronics or medical devices—can use expendable packaging fitted with foam assemblies to ensure items arrive safely. Although these assemblies are not intended for reuse, they offer an efficient single-use option when sterilization, contamination risks, or stringent product regulations come into play.
Advantages and Applications of Returnable Packaging
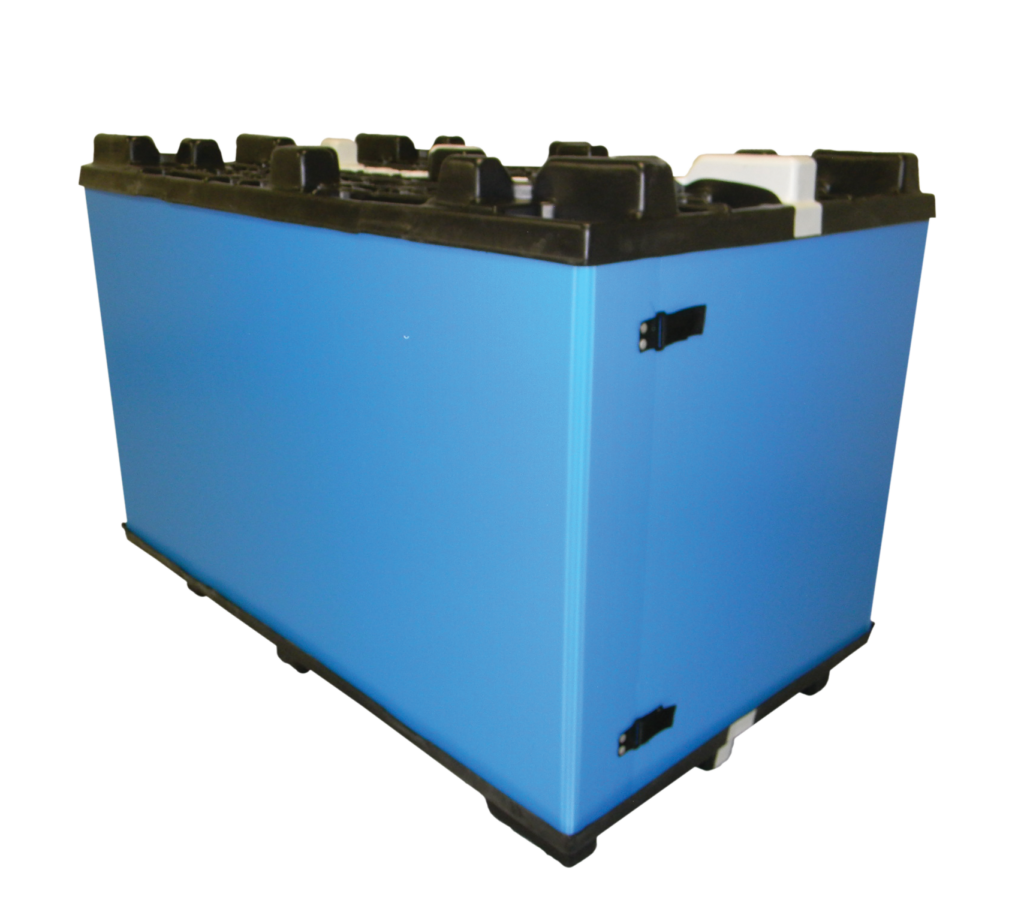
Returnable (or reusable) packaging is manufactured from sturdier materials that withstand multiple cycles of transport and handling. While it demands a bigger initial outlay, its long-term efficiency makes it an attractive choice for companies invested in sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
Long-Term Savings and Better ROI
Over time, a reusable solution spreads its initial cost across many shipping cycles, which lowers the per-use expenditure. This approach is especially advantageous for companies that frequently send goods along the same routes or within closed-loop supply chains where containers return for continuous reuse.
Sustainability and Environmental Responsibility
Returnable packaging offers a direct path to reducing waste. Instead of discarding materials after one trip, businesses can repeatedly repurpose containers or totes. This helps fulfill corporate social responsibility goals and meets the growing demand for eco-friendly supply chain practices. Many companies adopt strategies aligned with sustainable packaging strategies to cut down on single-use waste.
Enhanced Durability
By design, reusable packaging leverages heavier-grade plastics, metals, or corrugated plastic that endure wear-and-tear across many shipments. Items like plastic totes or steel racks survive rough handling and deliver consistent product protection, making them a reliable choice for industries dealing with bulky or high-value products.
Who Benefits Most
- Automotive and manufacturing: Large volumes and repetitive shipping routes benefit significantly from reusable containers.
- Electronics and appliance suppliers: Durable shipping solutions preserve sensitive or high-value products.
- Construction and military applications: Reliable, long-lasting containers protect materials needed for critical operations.
Sustainability Considerations in Packaging Decisions
Environmental objectives are key priorities for many businesses choosing modern packaging solutions. As part of a company’s broader approach to minimizing its ecological impact, packaging systems can be fundamental in achieving both practical and sustainability goals.
Reducing Waste and Resource Use
Reusable packaging extends product life and curtails waste headed to landfills. Even though some expendable solutions can be recycled, they often require frequent replenishment. Returnable systems stay in circulation for months or even years.
Material Efficiency and Eco-Friendly Innovations
Robust materials such as polypropylene are continuously refined. New formulations maintain strength but reduce weight, lowering shipping costs and overall carbon footprint. For instance, see comparisons of Polyethylene vs Polypropylene.
Practicality vs. Green Priorities
For one-way shipments or irregular routes, expendable solutions may still be less logistically complex. However, businesses with an overarching commitment to sustainability frequently adopt a blend of reusable containers and environmentally conscious single-use materials to balance practical needs and eco-friendly targets.
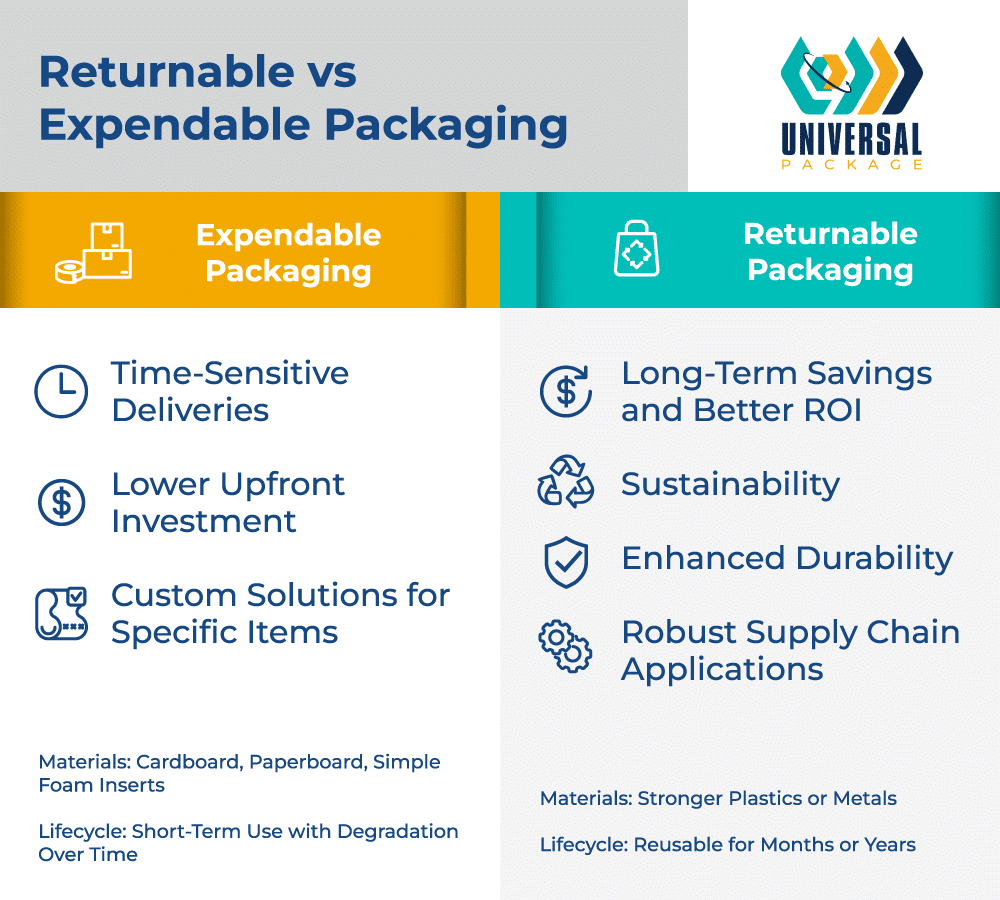
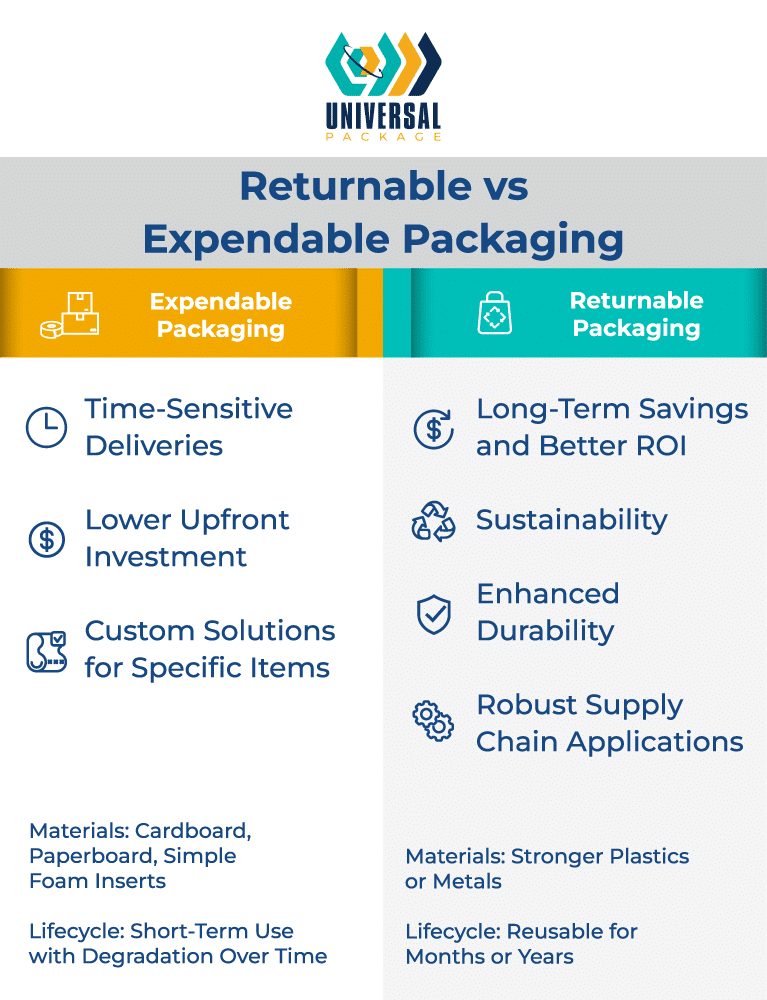
Factors to Consider When Choosing Between Expendable and Returnable Packaging
Selecting the right packaging method calls for a thorough evaluation of your operational demands, product characteristics, sustainability commitments, and financial constraints.
Operational Breakdown
Analyze your shipping routes, frequency, and distances traveled. If your logistics revolve around one-way shipments across long distances or to areas where returns are impractical, expendable packaging is often the best solution. On the other hand, dense local networks with repeated routes are primed for a returnable model.
Budgetary and Lifecycle Costs
Although expendable materials carry lower upfront costs, these expenses can multiply if you have ongoing shipping needs. Returnable packaging spreads the investment out through repeated use. Over time, reuse can yield meaningful savings, but factor in potential costs tied to cleaning and returning containers.
Product Demands
Fragile or specialized goods sometimes need customized cushioning, which can be implemented in expendable or returnable formats. Heavier, durable products often thrive with reusable systems due to their robust container environments. For items that ship repeatedly—like automotive components or high-volume retail products—returnable packages can deliver steady, reliable protection.
Future-Focused Goals
If your organization sets progressive targets for responsible resource use, returnable packaging may align more seamlessly with your sustainability roadmap. Meanwhile, a business testing new markets or shipping lanes might lean on expendable solutions until stabilized routes emerge. If your organization is looking to transition from expendable to returnable packaging, consider getting expert guidance from a dedicated team.
Considering a Hybrid Approach
Many companies employ a blended system, utilizing returnable containers for well-established routes while still leveraging expendable options for sporadic or international deliveries. For an extended look at how these strategies can work together, consult expendable to returnable packaging insights.
Making the Right Packaging Choice for Your Business Needs
Expendable and returnable packaging each offer tangible benefits for diverse shipping and storage needs. Expendable packaging may be best if your firm relies on one-way shipments, short-term demand, or limited reuse opportunities. Meanwhile, returnable models promise long-term cost savings, sturdier protection, and significant advantages in sustainability for businesses that regularly move goods in recurring loops.
For many organizations, a hybrid approach blends single-use and reusable solutions, aligning practical requirements with environmental and financial objectives. Universal Package has extensive experience across various industries and can help design a tailored program that meets your exact needs. Contact us to discuss custom packaging solutions that support your operational goals, from single-use applications to enduring reusable systems.