In the world of manufacturing and product distribution, the packaging is not just about aesthetics. It holds a far more pivotal role in safeguarding the product, facilitating effective transportation, and influencing consumer interaction. Understanding the distinct roles and functions of primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging is crucial in creating an efficient packaging strategy that ensures product integrity and boosts market appeal. This blog post aims to demystify these three levels of packaging, providing clear definitions, examples, and exploring their unique importance in the product supply chain. Packaging plays a critical role in product preservation and marketability. Even the minor details can have major implications for your business, from legal requirements to customer appeal. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of packaging types.
Understanding the Basics of Packaging Types
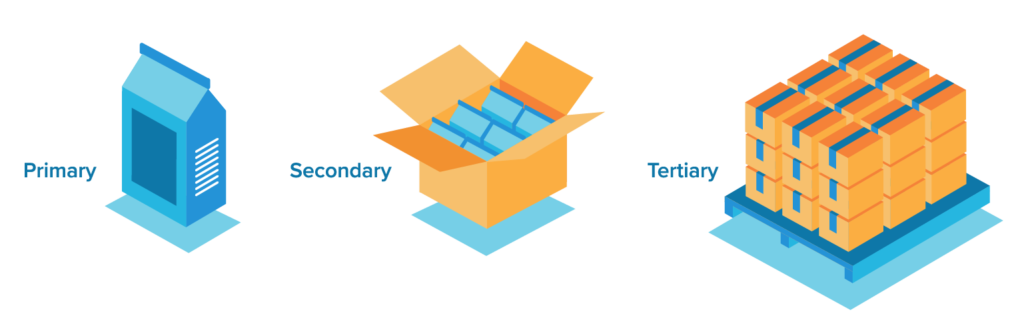
Packaging, in its simplest form, serves as a protective layer for products. However, it goes beyond just protection. It also plays crucial roles in product handling, storage, transportation, and marketing. Understanding the basics involve recognizing three major types – primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging.
Primary packaging is what directly encases the product, designed for the end consumer. It plays a pivotal role in product presentation and usability. Secondary packaging, on the other hand, is additional packaging that protects or consolidates the primary packages. It often communicates brand and product information and is an essential tool in retail settings.
Tertiary packaging, also known as transport or bulk packaging, is used to facilitate the handling and transportation of a series of sales units or secondary packages. It ensures the product’s protection during its transit and storage. By understanding each packaging type’s role, businesses can make informed decisions on their product packaging needs.
Delving into Primary Packaging
Primary packaging is the first layer of packaging in which the product is directly enclosed. This layer comes into immediate contact with the product and is often the package that consumers handle when using the product. Primary packaging is particularly crucial in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic sectors where maintaining product integrity and safety is paramount.
Examples of primary packaging are numerous, ranging from the plastic wrap around a loaf of bread, the bottle containing a soft drink, the lipstick tube, or the blister pack for a set of pills. Each of these packaging examples is designed to protect the product from external factors like moisture, light, and bacteria, while also providing a means for consumers to use the product effectively.
The importance of primary packaging lies in its direct interaction with the consumer. It serves as the first point of contact with your target audience. An effective packaging design must contain information that is useful to the consumer, displayed in a manner consistent with your brand’s identity. This includes elements like product information, instructions for use, and branding.
Exploring Secondary Packaging
Secondary packaging is the layer of packaging that encloses the primary packaging, offering added protection and often serving as the retail display unit. This type of packaging is often used to contain multiple primary packages, allowing retailers and customers to conveniently purchase or transport them. Secondary packaging is commonly used when multiple primary packaged items need to be grouped together.
Examples of secondary packaging include cereal boxes that hold bagged cereal, a cardboard box containing multiple canned goods, or a display box that houses individual candy bars. The packaging is designed to keep primary packaged products together, providing added protection during transit and making it easier for retailers to display.
Secondary packaging also plays a crucial role in brand promotion and customer attraction. Retailers often use the secondary packaging for display purposes, making it an essential part of the marketing mix. The packaging should be attractive, informative, and creative in order to stand out on store shelves. The packaging should also convey useful product information that helps the customer to make an informed shopping decision.
Lastly, secondary packaging is crucial in ensuring product safety. It serves as an additional protective layer that helps prevent damage, contamination, or product tampering. It is particularly critical for delicate or fragile products, or those with stringent safety requirements. Thus, secondary packaging serves a dual purpose: it safeguards the product and its primary packaging, and it serves as a valuable marketing tool.
Unveiling Tertiary Packaging
Tertiary packaging, often overlooked but equally essential, serves as the final layer that safeguards products during transportation and storage. This type of packaging is designed to protect large quantities of products, ensuring they remain intact while being transported from the manufacturer to warehouses, retail outlets, or distribution centers.
A typical example of tertiary packaging is the corrugated plastic boxes used to contain multiple units of a product. These items are utilized for their durability and ability to withstand long-distance shipping and handling.
The importance of tertiary packaging is most apparent in logistics and bulk transportation. It is responsible for ensuring that large quantities of products arrive at their destination in the same condition they left the manufacturer. Thus, it plays a crucial role in preventing damage and loss, significantly impacting a company’s bottom line.
Additionally, tertiary packaging also aids in efficient storage. By grouping products together, it allows for easier inventory management and space utilization in warehouses. This boosts productivity and helps to minimize wasted storage space.
The Interrelation of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Packaging
Understanding how primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging interconnect is integral in optimizing product safety, visibility, and transportation. Each level of packaging serves a distinct purpose, but they all function symbiotically to protect the product at different stages of its lifecycle.
Primary packaging directly houses the product, providing the first line of defense against potential damages. It is designed to safeguard the product while enhancing its aesthetic appeal, which is crucial for consumer interaction and brand recognition.
Secondary packaging, on the other hand, encases the primary packaging, offering an additional layer of protection. It also serves retail and marketing purposes, prompting customers to purchase the product. This layer often contains branding, nutritional information, instructions, and other relevant details that help consumers make informed purchasing decisions.
Tertiary packaging, the outermost layer, is designed for bulk handling, storage, and transportation. It ensures that both primary and secondary packaged products are securely bundled together for logistical purposes, minimizing damages during transit and facilitating efficient handling and storage.
The coordination among these three packaging levels is vital for product preservation, optimal shelf presentation, and efficient logistics. An imbalance or neglect of one level could compromise the effectiveness of the entire packaging process. Thus, it’s critical to give due attention to each packaging tier, ensuring they all function harmoniously to deliver the product in the best possible condition.
Choosing the Right Packaging for Your Product
Selecting the appropriate packaging for your product is fundamental to its safety, marketability, and transportation efficiency. It is not a decision to be taken lightly, as the packaging can greatly influence a product’s overall success. Therefore, a number of factors must be carefully considered to ensure the packaging type aligns with the product’s requirements and the company’s objectives.
Firstly, the product’s nature and characteristics should guide the packaging choice. Fragile items require more protective packaging, while perishable goods may need packaging with temperature control features. Similarly, the size and weight of the product are also crucial considerations.
Secondly, regulatory requirements and standards in your industry should shape your packaging decisions. Every industry has its unique requirements, so staying up-to-date on prevailing standards and guidelines is essential.
Thirdly, consider the packaging’s impact on your product’s visibility and presentation. For instance, primary packaging often acts as a marketing tool, so it should reflect your brand’s identity and appeal to your target audience.
Lastly, consider the logistics and transportation of your product. The right packaging should facilitate easy handling, storage, and transportation, reducing overall logistical costs. For instance, tertiary packaging, such as crates or pallets, is crucial for bulk transportation and can significantly influence transportation efficiency.
Remember, the ultimate aim is to choose a packaging type that preserves the product’s integrity, upholds regulatory standards, enhances product visibility, and promotes efficient transportation and storage.
Case Study: Successful Packaging Strategies
In the realm of packaging, real-world examples can be enlightening. Let’s take the case of a global beverage company. This company uses primary packaging in the form of glass bottles, which hold the actual drink. The label on the bottle, carrying the brand name and other product details, serves to attract and inform consumers.
For their secondary packaging, they utilize cardboard six-pack holders. Not only does this provide additional protection to the glass bottles, but it also offers convenience for customers carrying multiple bottles. Additionally, the holders carry branding and product information, boosting the company’s marketing efforts.
Tertiary packaging comes into play when these six-packs need to be transported from the factory to retail outlets. They are packed in large, sturdy cardboard boxes and wrapped with plastic for added security during transit. This level of packaging ensures the safe and efficient transportation of the products, minimizing the risk of damage.
Through this strategic use of all three levels of packaging, the beverage company has been able to successfully protect their product, enhance consumer experience, and streamline their logistics. This case clearly demonstrates how primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging can work together effectively when properly coordinated.
Packaging Solutions with Universal Package
Universal Package is a dedicated provider of comprehensive packaging solutions tailored to meet specific industry needs. Leveraging extensive experience and cutting-edge technology, we offer an array of services ranging from primary and secondary packaging material production to intricate tertiary packaging designs.
Our team is committed to delivering quality and innovation at each packaging level. We offer a wide selection of materials including plastic, metal, and paper for primary packaging purposes.
Whether you’re a manufacturer or a trade show exhibitor, Universal Package can help you make an informed decision about your packaging needs. We offer consulting services that guide you through the process of selecting the appropriate packaging type for your product, considering factors such as product safety, transportation efficiency, and retail display requirements.
In addition, Universal Package stays abreast of the latest trends and regulations in the packaging industry. We continuously innovate our services to meet evolving market demands and ensure our clients stay ahead of the competition. Trust in Universal Package to provide reliable, high-quality packaging solutions for your business.
Conclusion
As we’ve uncovered, understanding the variances between primary, secondary, and tertiary packaging is key to ensuring product safety, optimizing transportation, and enhancing consumer interaction. Selecting the right packaging type can significantly contribute to your product’s success, from the warehouse to the retailer’s shelf.
At Universal Package, we understand how crucial this decision is, and we’re committed to helping you navigate this complex landscape. Our extensive range of packaging products and services cater to every level of packaging needs, providing both standard and custom solutions that ensure durability and safety.
So, when considering your next packaging solution, remember: the right choice can make all the difference. Let’s choose wisely together. Reach out to us at Universal Package, and let us guide you in exploring all types of packaging that best suit your product’s needs. We’re ready to assist with our expertise, innovative solutions, and dedicated services