When it comes to safeguarding sensitive electronic components during transit, storage, or handling, the choice of packaging material plays a critical role. The goal is to protect electronics from damage caused by physical shocks, vibrations, static electricity, or environmental factors like moisture and temperature fluctuations. To achieve this, two popular material options have emerged as top contenders: foam and thermoformed plastic.
Each material offers distinct advantages and considerations that influence its suitability for specific use cases. Foam packaging excels at cushioning and shock absorption, making it ideal for fragile electronics. In contrast, thermoformed plastic is valued for its durability, precision, and reusability, which can provide advantages in high-volume or long-term applications. Understanding the unique characteristics of these materials will help you make an informed decision tailored to your needs.
In this article, we’ll examine the core properties of foam and thermoformed plastic packaging, explore their respective strengths and weaknesses, and outline critical factors to consider when deciding which material is right for your electronics. Let’s dive into the details and discover how these materials stack up.
The Importance of Electronics Packaging
Electronics are among the most delicate products, highly susceptible to damage caused by physical impacts, vibrations, and environmental stressors like temperature changes and moisture. Without proper packaging, even minor shocks during transit or storage can render sensitive components inoperable. Additionally, many electronic devices are vulnerable to electrostatic discharge (ESD), which can cause irreparable harm or system malfunctions.
Effective electronics packaging is essential to prevent such risks and ensure the integrity of the products from production to end use. Failure to protect electronics adequately can lead to costly outcomes such as damaged goods, dissatisfied customers, and avoidable disruptions in the supply chain. On the other hand, smart packaging strategies help businesses safeguard their products, minimize losses, and maintain strong customer relationships.
Well-designed packaging doesn’t just protect products—it enhances overall logistics efficiency. Solutions like stackable or nestable containers, including plastic bulk containers, can help maximize storage space and reduce the effort required for handling items. This optimization can result in smoother workflows and lower costs, critical for businesses aiming to stay competitive in today’s markets.
Beyond functionality, electronics packaging reflects a company’s professionalism and brand identity. Packaging that ensures products arrive securely and intact showcases a company’s commitment to quality. Environmentally friendly packaging solutions—such as reusable packaging options—further demonstrate a forward-thinking approach, appealing to customers who value sustainable practices.
Ultimately, tailored and robust electronics packaging goes far beyond protecting the product—it helps businesses uphold their reputation, achieve operational efficiency, and meet customer expectations in a competitive, high-stakes global marketplace.
Overview of Foam Packaging Assemblies for Electronics
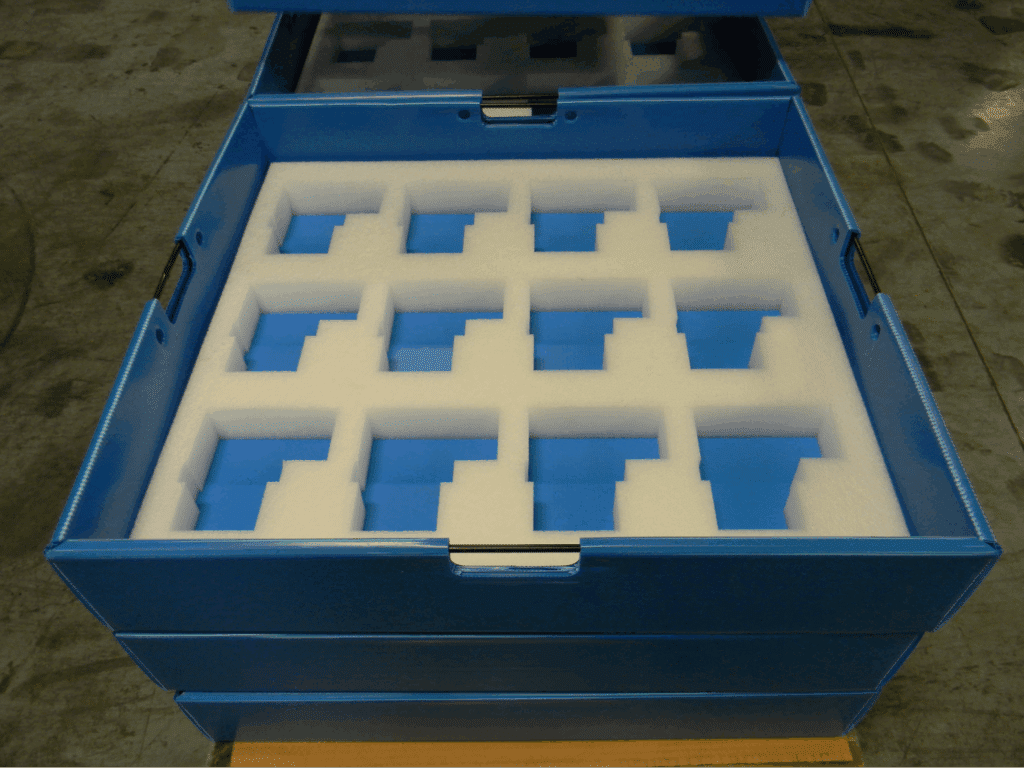
Foam packaging assemblies are widely recognized for their exceptional ability to cushion, absorb shock, and dampen vibrations, making them a trusted choice for protecting electronic components. Whether it’s fragile consumer devices or heavy industrial equipment, foam creates a protective barrier that minimizes movement and shields products from impacts during shipping, handling, and storage.
Foam packaging assemblies vary in density and composition, offering a broad range of solutions for electronics.
Properties of Foam as a Packaging Material
Foam is manufactured by infusing air into plastic- or rubber-based materials, creating a flexible, lightweight substance with unique protective qualities. Various types of foam—like polyurethane (PU), polyethylene (PE), and expanded polystyrene (EPS)—cater to different packaging needs, offering options in density, compressibility, and resilience. These characteristics can be customized during production to meet specific requirements.
- Shock Absorption: Foam compresses upon impact and gradually rebounds, spreading the energy over time to reduce the force felt by the packaged product.
- Vibration Dampening: Certain foam designs stabilize products during prolonged transit or repeated handling, reducing the risk of damage.
- Moisture Resistance: Some foam materials resist moisture absorption, providing added defense against humidity.
- Custom Shaping: Foam can be precisely designed to fit irregularly sized electronics, ensuring a snug and secure encasement.
For additional short-term solutions, businesses may also consider expendable packaging, which serves as an economical approach to one-way shipments.
Advantages of Foam Packaging Assemblies
- Exceptional Cushioning: Foam excels at protecting sensitive electronics by absorbing shocks and providing a soft barrier against rough handling. This feature is critical for delicate circuit boards, microchips, and sensors.
- Versatility in Density and Application: Foam is available in a range of densities to match different product needs. Lightweight closed-cell foam suits small consumer electronics, while denser foams protect heavier industrial equipment.
- Electrostatic Protection: Anti-static and conductive foam variants are designed to prevent ESD, safeguarding electronics vulnerable to static charges. This is especially important for components like computer processors or other highly sensitive assemblies.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Foam remains an economical choice for short-term or single-use packaging. It offers reliable protection without requiring significant capital investments.
Disadvantages of Foam Packaging Assemblies
- Limited Durability: Foam may lose its cushioning properties through repeated use and wear, reducing its long-term effectiveness.
- Reduced Reusability: Frequent shipping cycles can degrade foam’s structure, which makes it less suitable for applications needing durable, long-lasting packaging.
- Environmental Concerns: Traditional foam materials are often not biodegradable, posing sustainability challenges. Eco-friendly variants exist but are still emerging in the market.
Foam packaging delivers high-performance protection through flexibility, shock absorption, and anti-static properties. Its unique advantages make it ideal for many short-term, low-volume applications, although businesses must balance these benefits against foam’s shorter lifespan and potential environmental drawbacks.
Overview of Thermoformed Plastic Packaging for Electronics
Thermoformed plastic packaging is an increasingly popular solution for electronics, offering precision and durability. This packaging type is produced by heating thin sheets of plastic until they’re malleable, then shaping them into specific forms using tooling and molds. Once cooled, the material solidifies into a rigid, custom-fitted package.
Properties and Customization Capabilities
Thermoformed plastic can be produced from various materials, such as PET, PVC, HIPS, or ABS, each boasting different strengths and costs. These substrates can be tailored to create packages like trays, clamshells, and other specialized designs that nest components securely in place.
Thermoformed Plastic Packaging stands out for its ability to form precise compartments or cavities, helping to reduce movement during transit.
Advantages of Thermoformed Plastic
- Strength and Durability: Thermoformed plastic’s rigidity ensures that it can withstand repeated handling, making it suitable for demanding environments or high-traffic supply chains.
- Reusability for Cost Efficiency: In closed-loop systems, thermoformed plastic retains its structure through numerous shipping cycles, delivering cost savings in the long run. If you are looking for a more extended service life, pairing it with Clean & Repair services can help maintain quality over time.
- Professional Presentation and Organization: A precisely molded interior keeps electronic components organized. This benefit not only protects against jostling but also promotes a polished, professional look.
- Sustainability Through Longevity: With proper care, thermoformed plastic can be reused multiple times, limiting waste. Utilizing recyclable materials further aligns this approach with environmental goals.
Disadvantages of Thermoformed Plastic
- Higher Initial Investment: Custom tooling and mold production can lead to a challenging upfront expense. However, for businesses with sizable or ongoing packaging needs, these costs may be offset by repeated use.
- Reduced Shock Absorption: Thermoformed plastic secures items in place, but it doesn’t inherently provide the cushioning found in foam. Highly fragile electronics may require supplemental padding.
- Complex End-of-Life Management: Recycling depends on the specific type of plastic and local capabilities. Selecting a commonly recycled plastic can help mitigate this issue.
Thermoformed plastic packaging excels in scenarios where long-term durability, reusability, and precise organization are paramount.
Key Comparisons Between Foam and Thermoformed Plastic
Selecting the right material for your electronics hinges on considerations like durability, protective qualities, cost, and environmental impact. Below is a side-by-side comparison:
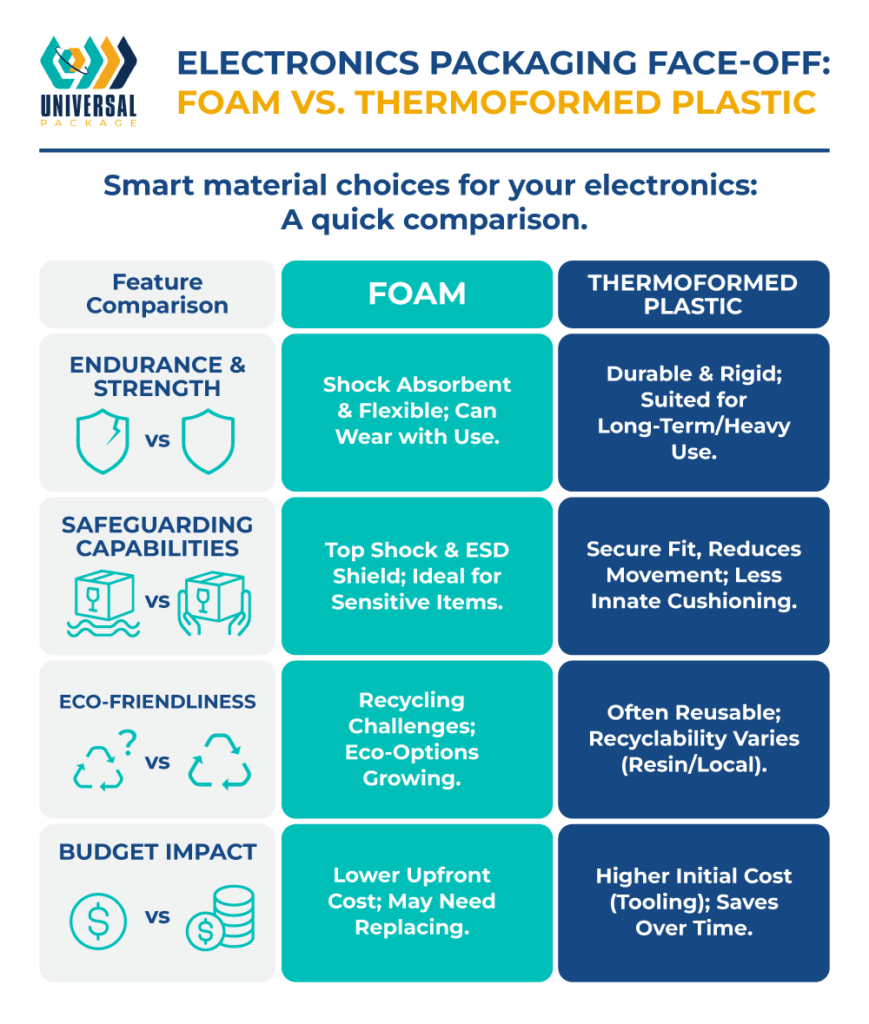
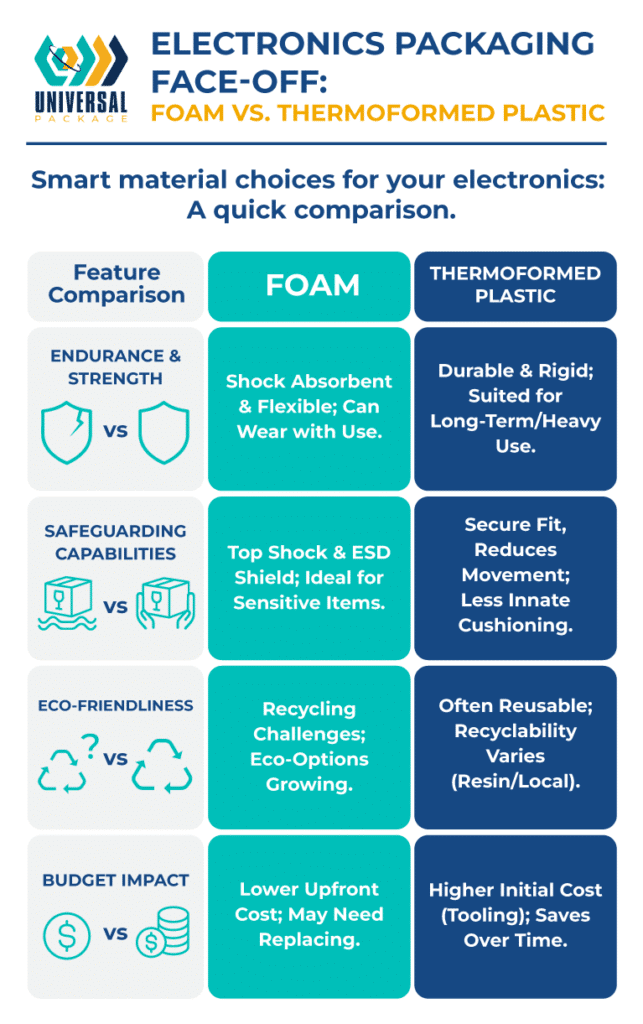
Durability
- Foam: Offers excellent flexibility and shock absorption but may wear out with repeated use.
- Thermoformed Plastic: Provides a rigid structure suited to long-term or high-volume applications.
For items requiring extra structural support, businesses often opt for steel racks or custom dunnage solutions to further bolster durability.
Protection Capabilities
- Foam: Excels in shock absorption and ESD mitigation, making it great for delicate systems.
- Thermoformed Plastic: Offers a secure fit to prevent movement, though less cushioning.
- Trays and Pads: Supplementing thermoformed packages with foam trays & pads can bridge the cushioning gap.
Environmental Considerations
- Foam: Traditional varieties can be challenging to recycle, though newer eco-friendly foams are emerging.
- Thermoformed Plastic: Reusable and potentially recyclable, contingent on resin type and local recycling infrastructures.
Cost
- Foam: Features a lower initial outlay for single-use scenarios. Over multiple shipments, replacements can add up.
- Thermoformed Plastic: Involves higher upfront costs due to tooling, yet savings accrue over time in repeated-use systems.
When seeking a broader set of packaging tools, options like kitting totes and hand totes might be suitable complements to both foam and thermoformed solutions, offering flexibility in logistics processes.
When to Choose Foam vs. Thermoformed Plastic
Different applications demand distinct packaging approaches. Below are scenarios highlighting which material may fit best, though a hybrid strategy can sometimes be the ideal.
Foam: Ideal for High Fragility and Short-Term Applications
- Delicate Components: Foam’s cushioning is preferable for microchips, sensors, and circuit boards sensitive to impacts.
- Single-Use or One-Way Shipments: For shipments unlikely to need return, foam is a cost-effective, dependable travel companion.
- Temporary Packaging Needs: When packaging use is brief or volume is low, foam’s primary advantage is its robust shock absorption.
- Specialized Protection: Anti-static or conductive foam precautions guard against electrostatic hazards.
Additionally, foam works well in Packaging for Transportation that prioritizes lightweight yet protective options.
Thermoformed Plastic: Best for Long-Term Use and Reusability
- Frequent Handling and Reuse: Thermoformed plastic maintains structural integrity across numerous shipping cycles, reducing total packaging expenditures.
- High-Volume and Long-Term Applications: Thanks to precise shaping and strength, it’s a go-to for businesses shipping large batches regularly.
- Manufacturing and Assembly Efficiency: Components are neatly arranged, speeding up fulfillment and reducing errors.
- Professional Presentation: A neat, uniform layout supports brand consistency and reliability.
If ongoing access to packaging is desired without large capital investment, Lease & Rental Options can further extend thermoformed plastic’s value in repeated-use channels.
Finding the Right Balance
A hybrid solution that uses foam inserts within thermoformed plastic trays can combine shock absorption with structural stability. This approach brings together the benefits of both materials, offering a tailored method for specific product requirements. Additionally, for smaller electronics and in-plant handling, Plastic Totes can serve as a lightweight, customizable solution that pairs well with either foam or thermoformed plastic inserts.
Advantages of Customization in Electronics Packaging
Off-the-shelf packaging often struggles to accommodate specialized electronics or unique product forms. By contrast, customized solutions can adapt to specific shapes, sizes, and handling needs:
- Precise Fit for Maximum Protection: Packaging tailored to device dimensions eliminates wasted space, minimizing vibration and breakage risks.
- Integrated Anti-Static Features: Custom designs can add anti-static or conductive elements for ESD-sensitive devices, ensuring a higher level of safety.
- Enhanced Branding Opportunities: Personalized colors, logos, and graphics allow packaging to double as a brand ambassador, especially in B2B or end-user markets.
- Streamlined Operational Efficiency: With compartments and cavities built to spec, assembly and picking processes become more efficient, saving time and labor costs.
- Optimized Lifecycle Management: Tailored designs account for transport conditions, shipping frequency, and potential storage intervals for a more effective and consistent product lifecycle.
- Scalable Sustainability: Solutions can incorporate recyclable materials or focus on reusability, reducing waste and meeting eco-conscious objectives.
Whether you’re using foam, thermoformed plastic, or a combination of both, customization ensures that packaging solutions directly address the unique challenges of modern electronics.
Protect and Enhance Your Products Effectively With Universal Package
Selecting the ideal packaging material for electronics is a critical decision that directly influences product safety, operational efficiency, and brand reputation. Foam packaging offers excellent shock absorption and cushioning, making it well suited for delicate or short-term applications. Thermoformed plastic wins favor for its durability, precision, and reusability—qualities that hold particular merit in long-term, high-volume settings.
In many instances, a hybrid approach that leverages the cushioning of foam inserts alongside the rigidity of thermoformed plastic can deliver the best of both worlds. By customizing packaging to match your devices’ fragility, shipping demands, and sustainability goals, you position your business for efficient, secure, and cost-effective results.
If you’re ready to explore customized packaging solutions that truly meet your electronic packaging challenges, consider partnering with Universal Package. For more than twenty years, their expertise in creating secure and reliable packaging can help protect your products and enhance your competitive edge. Contact the experts at Universal Package today to learn more about their customized packaging solutions.