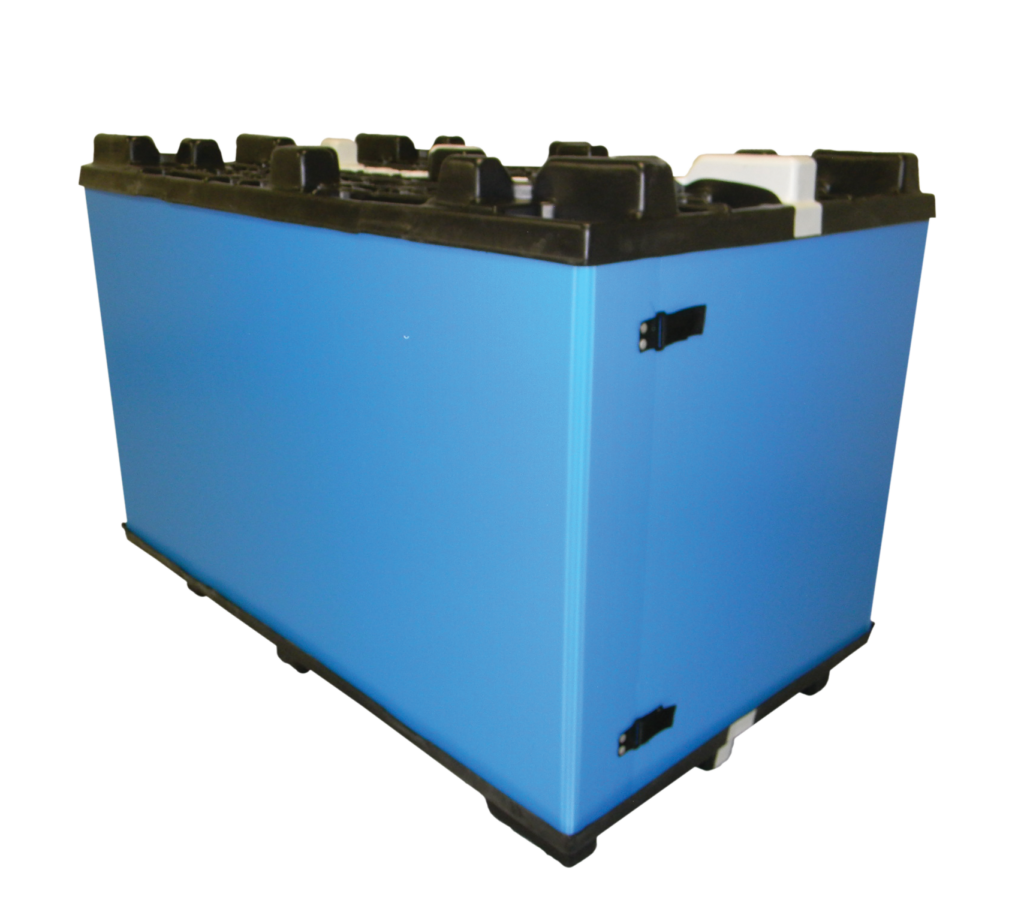
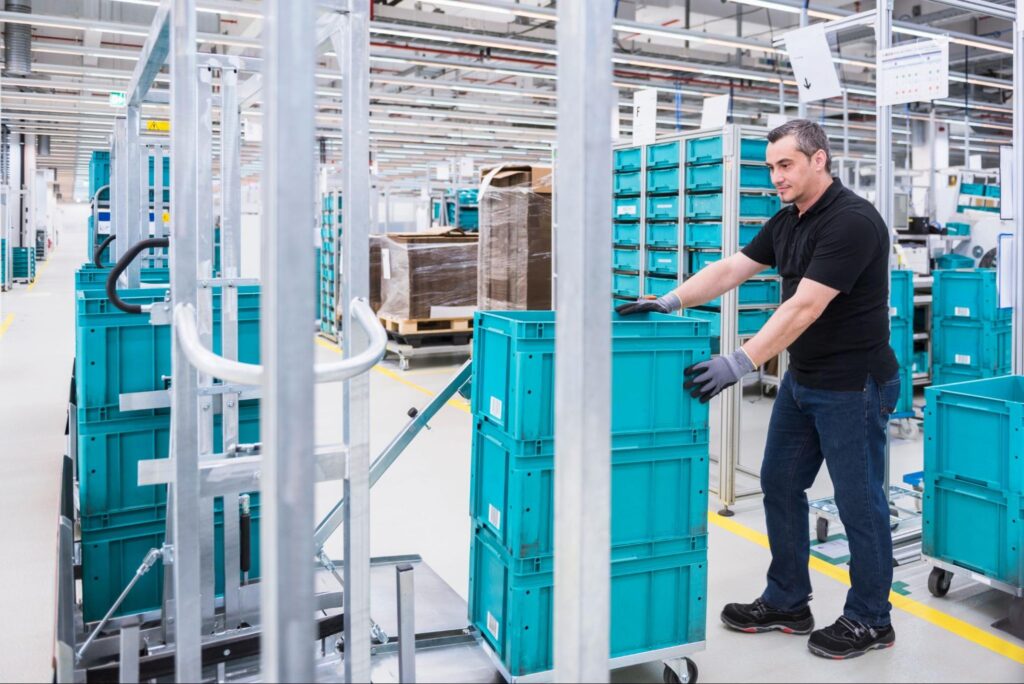
Rigid packaging is much more than a container—it is a strategic tool for enhancing product security and streamlining operations. These solutions are defined by their solid, resilient materials, such as hard plastics, metals, and glass, which allow them to maintain their form under heavy loads and resist collapsing.
This structural integrity is critical in today’s fast-evolving supply chains, where ensuring goods remain secure through challenging conditions is paramount. In this article, we explore the benefits of rigid packaging as well as the materials and industries that can best leverage its potential. We also outline the steps to successful adoption, emerging trends, and the future outlook for the industry.
Key Benefits of Rigid Packaging
Modern businesses face a myriad of challenges, from rising consumer expectations to increasingly complex supply chains. Rigid packaging, when deployed strategically, can alleviate many of these issues while adding value in several key areas. By integrating durable materials and thoughtful design, companies can establish more resilient supply chains.
Superior Durability and Enhanced Protection
Rigid packaging withstands deformation and protects goods from impacts, moisture, and heavy loads. Industries like electronics or medical devices rely on this construction to prevent damage in transit. In many cases, choosing sturdy materials such as hard plastics or metals can contribute to fewer returns and replacements by enhancing the protection of items during shipping.
Long-Term Reusability and Cost Considerations
Although rigid packaging usually comes with a higher upfront cost, its extended lifespan contributes to fewer replacements or repairs. While direct research on quantifiable long-term savings is still evolving, a reduction in waste and inventory loss often supports total cost efficiency.
Customizable Designs for Strong Branding
Rigid packaging is highly adaptable, offering features like adjustable compartments, tamper-resistant seals, and sophisticated graphics. This flexibility helps companies boost their brand identity by linking packaging aesthetics to their core values. Businesses seeking specialized layouts can opt for corrugated plastic containers or foam assemblies, which allow them to optimize the interior configuration as well as the exterior look.
Robust Security Features
Industries handling pharmaceuticals, medical supplies, or high-value electronics require tamper-evident seals and sturdy closures, which rigid packaging naturally supports. This added level of security maintains product integrity from the production floor to the final destination.
Materials Commonly Used in Rigid Packaging
The long-term performance of rigid packaging hinges on its material composition. Each material caters to unique application requirements:
Hard Plastics
Hard plastics balance impact resistance with a lightweight form, benefiting retailers shipping delicate goods. They often incorporate foam inserts for extra shock absorption, providing a secure fit for fragile contents.
Metals
Metals, like steel or aluminum, excel in load-bearing and protective qualities. They are also highly recyclable, adding an environmentally responsible dimension to packaging strategies.
Glass
Glass containers suit brands seeking a premium look or chemical inertness, such as high-end food, beverage, and cosmetic products. Their recyclability and non-reactive nature remain prime advantages, although weight and fragility must be managed carefully.
Foam Inserts
High-density foam inserts secure products by stabilizing them against jostling or vibration. This cushioning is crucial when shipping medical devices or high-value electronics.
Textile-Plastic Hybrids
Combining fabric flexibility and sturdy plastic layers, these hybrid materials deliver a supportive structure and shock cushioning. They are ideal for specialized applications requiring both rigidity and gentle handling.
Industrial Applications of Rigid Packaging
Rigid packaging is critical across several industries, leveraging durability and reliability to address specific demands:
- Automotive: Protects heavy parts from mechanical stress and vibrations during distribution. Manufacturers often employ steel racks for secure shipping and storage.
- Electronics: Guards sensitive devices against shock, minimizing the risk of damage from external impacts.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: Maintains sterility and tamper resistance, both essential for life-saving products.
- Construction: Offers toughness and stability for oversized or heavy materials. Plastic totes can handle high-volume transport needs.
- Trade Shows and Events: Streamlines logistics with modular and reusable designs that simplify exhibit transport and setup, often supported by kitting totes.
By selecting the right configuration for each industry, operations can be optimized for both security and efficiency.
A Practical Guide to Adopting Rigid Packaging

Successfully introducing a rigid packaging system is a strategic process that moves from careful planning to a thoughtful rollout. A well-executed plan can determine the success of your packaging strategy by maximizing benefits while mitigating potential challenges.
Step 1: The Selection Process
The foundation of a successful program is choosing the right solution for your specific needs. This initial phase requires a thorough evaluation:
- Evaluate Product Needs: Begin by considering your product’s size, weight, fragility, and the degree of exposure it will face during transit. Sensitive or high-value goods often benefit from solutions with foam inserts or specialized compartments. For large-scale or short-term projects involving heavier goods, exploring lease & rental options for sturdy containers can be a practical starting point.
- Consider Material and Design Options: Weigh the distinct benefits of plastics, metals, and glass against your operational requirements. Look into advanced features like tamper-evident seals, adjustable compartments, or integrated foam to meet both functional and brand-related goals.
- Weigh Long-Term Benefits: Though the initial outlay can be higher, the reduced incidents of product breakage and fewer replacements contribute significantly to operational efficiencies and maximize your return on investment. Many companies find that focusing on reliability pays off in reduced damage claims and streamlined shipping procedures over time.
Step 2: Strategic Implementation
Once a solution is selected, a phased and strategic rollout ensures a smooth transition and maximizes performance.
- Begin with Pilot Testing: Before a broad deployment, trial your new packaging methods in a controlled environment. This allows you to gather data, identify potential issues, and refine processes without disrupting your entire operation.
- Integrate Smart Tracking: For more efficient inventory control, tag containers with RFID or NFC chips. This provides real-time tracking and inventory management abilities, which enhance visibility and traceability in the supply chain.
- Analyze Data for Performance Optimization: Leveraging the data gathered from your RFID or NFC tags, you can identify any potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies in your supply chain. By analyzing this information, you can further optimize your packaging strategy to increase productivity and reduce costs.
- Prioritize Staff Training: Instruct your teams on the correct procedures for handling, packing, and storing the new rigid containers. Proper training is essential for maximizing performance, ensuring operational safety, and extending the lifespan of your packaging assets.
Step 3: Navigating Challenges and Considerations
Adopting rigid packaging may present initial challenges, including higher upfront costs, the need for logistical adjustments, and additional staff training. However, these hurdles can be effectively managed:
- Mitigate Risks Proactively: These challenges can be mitigated by choosing the right materials and collaborating with a reputable supplier who understands your industry. Phased implementation, coupled with routine quality checks, allows companies to fine-tune their approach and manage costs effectively.
- Focus on the Justified Investment: Ultimately, the initial investment is often justified by the significant reduction in product damage and operational disruptions. This is why identifying the right supplier and leveraging their expertise in solving potential problems is essential.
- Collaborate with Key Players: Engage all stakeholders early on, from production and logistics teams to customers and suppliers. By gathering insights and addressing concerns, you can better anticipate and resolve potential issues before they occur.
The Role of Sustainability in Rigid Packaging
From regulatory compliance to environmental stewardship, sustainable packaging methods remain a priority for modern businesses. While not always biodegradable, rigid packaging fits squarely into sustainable practices through its emphasis on reusability and recyclability. Companies employing these strategies position themselves as both environmentally aware and operationally efficient. Key strategies include:
- Durability and Reusability: The extended lifespan of rigid packaging is its greatest environmental strength. Its durability means fewer replacements are needed, which significantly reduces the volume of waste generated compared to single-use alternatives.
- Recyclability: Many rigid materials can be reprocessed multiple times, supporting a circular economy. Materials such as metal, glass, and specific plastics can be efficiently recycled, helping to reduce disposable waste and lower the consumption of virgin resources.
- Complementary Strategies: Businesses can adopt a hybrid approach by integrating primary rigid packaging with expendable packaging such as biodegradable or fiber-based materials. This allows companies to curb landfill contributions and balance cost with environmental goals without compromising on protection.
Furthermore, businesses can extend the life cycle of their packaging assets through proactive maintenance. Utilizing clean & repair services for reusable containers, for instance, adds to their overall sustainability and maximizes the return on investment.
Emerging Trends in Rigid Packaging
Market dynamics continually shape the evolution of rigid packaging. Current trends aim to further enhance performance, security, and adaptability:
Evolution in Sustainable Practices
Sustainability holds center stage, with expanded use of reclaimed materials and circular economy methods to reduce waste. Although newer biodegradable options are in development, the recyclability of rigid packaging continues to serve as a vital eco-friendly element.
Smart Packaging Solutions
Real-time monitoring throughout the supply chain is increasingly enabled by RFID tags and NFC chips. These add-ons bolster security and traceability, ensuring consistent product quality across longer shipping routes.
Lightweight, Modular Designs
Innovation in material science is driving solutions that cut down on weight without sacrificing durability. Modularity helps businesses better manage storage space, particularly when transitioning to or from high-volume shipments.
Aesthetic Customization
Customization is no longer limited to functionality; embossed logos, creative color schemes, and tailored finishes are widely used. These fine touches help companies differentiate themselves in competitive markets.
Shaping the Next Generation of Rigid Packaging

The future of rigid packaging is being shaped by two powerful forces: continuous innovation within the industry and strategic collaboration among its key players. Together, these elements ensure that packaging solutions will continue to evolve to meet the complex demands of modern supply chains.
Future Outlook and Industry Innovations
Rigid packaging’s core strengths—security, longevity, and brand reinforcement—will remain compelling. Ongoing material innovations and digital tracking capabilities enrich the role of rigid containers across different sectors. For businesses adept at integrating these solutions into their workflows, the promise of stable growth and enhanced market positioning becomes more achievable.
Advancing Industry Collaboration
Industry-wide collaboration drives improvements in rigid packaging. By sharing technical insights, sustainability developments, and best practices, businesses and suppliers can push the boundaries of quality and efficiency. This cooperative environment aids in adapting to new regulations, optimizing supply chain performance, and meeting evolving consumer demands.
The Strategic Edge of Rigid Packaging for Modern Businesses
Rigid packaging stands out as a reliable option for enhancing product security, boosting operational efficiency, and strengthening brand presence. Its durability, potential cost benefits, and environmental adaptability make it a worthwhile investment plan.
If you’re interested in exploring customizable and sustainable rigid packaging solutions that can empower your operations and safeguard your products, reach out to Universal Package to learn more about the options that best meet your business objectives.