Medical device packaging is essential for protecting product integrity, ensuring sterility, and meeting ever-evolving regulatory standards. Manufacturers face new challenges in safety, durability, and logistics while adapting to updated guidelines.
This comprehensive guide delivers clear, actionable insights into best practices, compliance updates, and innovative strategies to ensure that your medical devices remain safe and effective throughout their lifecycle. Quality control professionals, regulatory officers, and product designers will find valuable strategies to secure supply chains, reduce risks, and maintain patient safety.
Key Considerations for Medical Device Packaging
Medical device packaging is a highly specialized discipline dedicated to protecting product integrity, ensuring sterility, and safeguarding patient safety. It involves a strategic process of selecting the right materials, engineering precise designs, and validating every step to shield devices from contamination and damage throughout their entire lifecycle—from the factory floor to the healthcare provider’s hands.
At its core, effective packaging must address several fundamental considerations simultaneously:
Safety and Product Integrity
The primary goal is to protect the device from physical hazards like shocks, vibration, and compression, as well as environmental challenges like temperature fluctuations, humidity, and contaminants. High-performance materials such as corrugated plastic, custom foam assemblies, and reinforced containers are chosen to provide robust impact resistance and ensure the device arrives in perfect condition.
Sterilization Compatibility
Packaging materials must withstand the chosen sterilization method—be it ethylene oxide (EtO), gamma irradiation, or autoclaving—without degrading or compromising the sterile barrier. Compliance with standards like ISO 11607 is crucial to guarantee that the package can maintain sterility from the point of sterilization to the point of use.
Durability and Reusability
For devices requiring long-term storage or frequent handling, durability is key. In many cases, reusable packaging solutions like reinforced containers or custom-designed sleeve packs offer a sustainable advantage. These solutions not only lower long-term costs and reduce environmental waste but can also be leased or rented to minimize upfront investment while maintaining full compliance.
Optimized Transportation and Storage
Logistics play a vital role in packaging design. By using lightweight yet strong materials and creating compact, load-bearing designs, manufacturers can significantly reduce shipping costs. Efficient design also maximizes warehouse space and protects devices from the physical stresses and environmental variations inherent in global supply chains.
Regulatory Compliance Features
Modern packaging must incorporate features that meet strict regulatory demands. This includes tamper-evident seals to ensure the sterile barrier has not been breached and clear, accurate labeling that supports traceability and provides essential information to the end-user.
The Core of Compliance: Risk Management, FDA QMSR, and ISO Standards
Navigating the medical device packaging landscape requires a deep understanding of a few foundational pillars of compliance. At the heart of every regulation is a commitment to patient safety, driven by proactive risk management and adherence to globally recognized standards.
The Central Role of Risk Management
Risk management is the proactive, systematic process of identifying and mitigating potential hazards across the entire packaging lifecycle. By embedding quality control directly into the process, manufacturers can anticipate and correct potential failures before they happen. This streamlines regulatory approvals and builds a more resilient and defensible quality system.
Key Regulatory and Quality System Frameworks
- FDA Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR): The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has modernized its requirements to harmonize more closely with global standards. The QMSR framework emphasizes a risk-based approach, requiring that risk management be an integral part of a manufacturer’s quality system. This means that every decision, from material sourcing to process validation, must be documented and justified based on its impact on product safety and effectiveness.
- ISO 13485:2016 standard – The Quality Management Gold Standard: This international standard specifies the requirements for a quality management system specifically for the medical device industry. Compliance with ISO 13485 demonstrates a commitment to quality that extends to packaging. It ensures that all processes—including design, validation, and traceability—are controlled, documented, and consistently reviewed for improvement.
- ISO 11607 – The Blueprint for Sterile Packaging: As the fundamental global standard for sterile medical device packaging, ISO 11607 is non-negotiable. It is divided into two parts:
- ISO 11607-1: Outlines the strict requirements for the materials and design of sterile barrier systems. It mandates that packaging materials must be compatible with the chosen sterilization method (e.g., EtO, gamma, autoclave) and capable of maintaining a sterile barrier over time.
- ISO 11607-2: Focuses on the validation requirements for forming, sealing, and assembly processes. It requires manufacturers to prove that their packaging processes are repeatable and consistently produce a sterile barrier that meets all specifications.
Adhering to these core principles and standards is not merely a box-ticking exercise; it is the fundamental way manufacturers ensure that their products are safe, effective, and trusted by healthcare providers and patients alike.
The Role of Custom Packaging Solutions in the Medical Industry
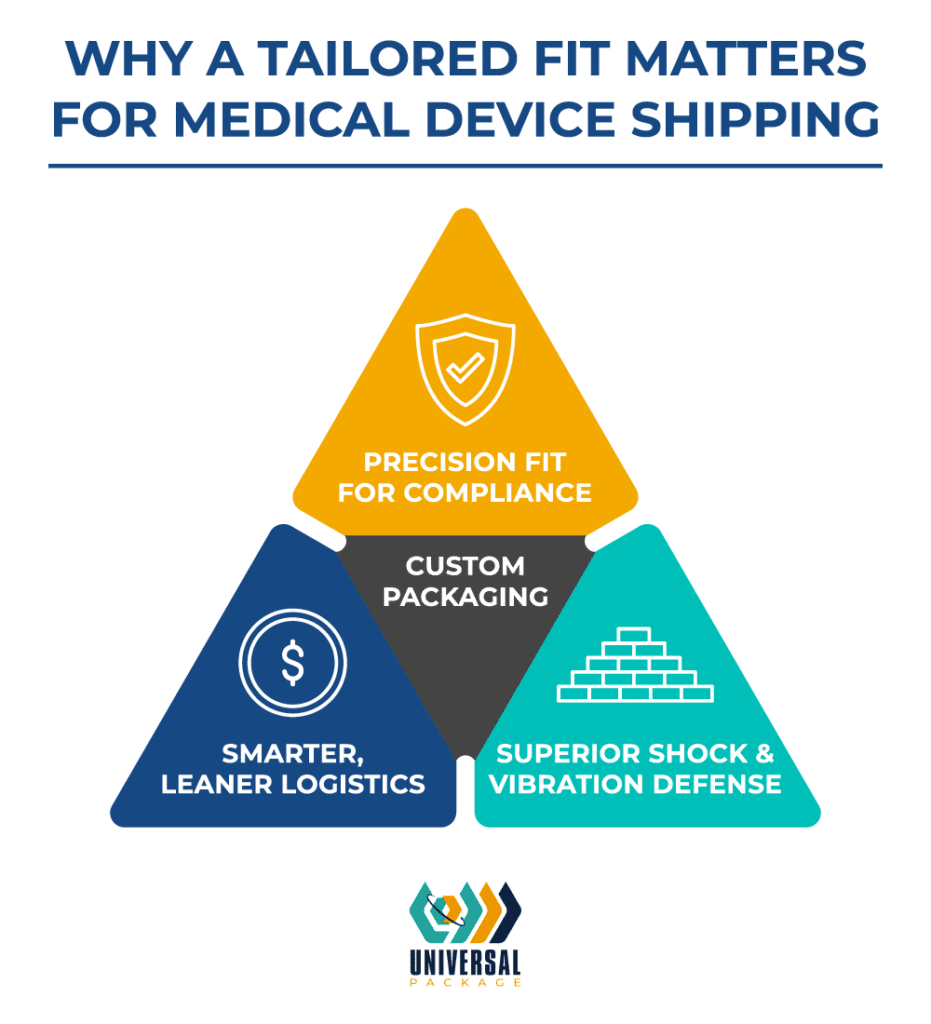
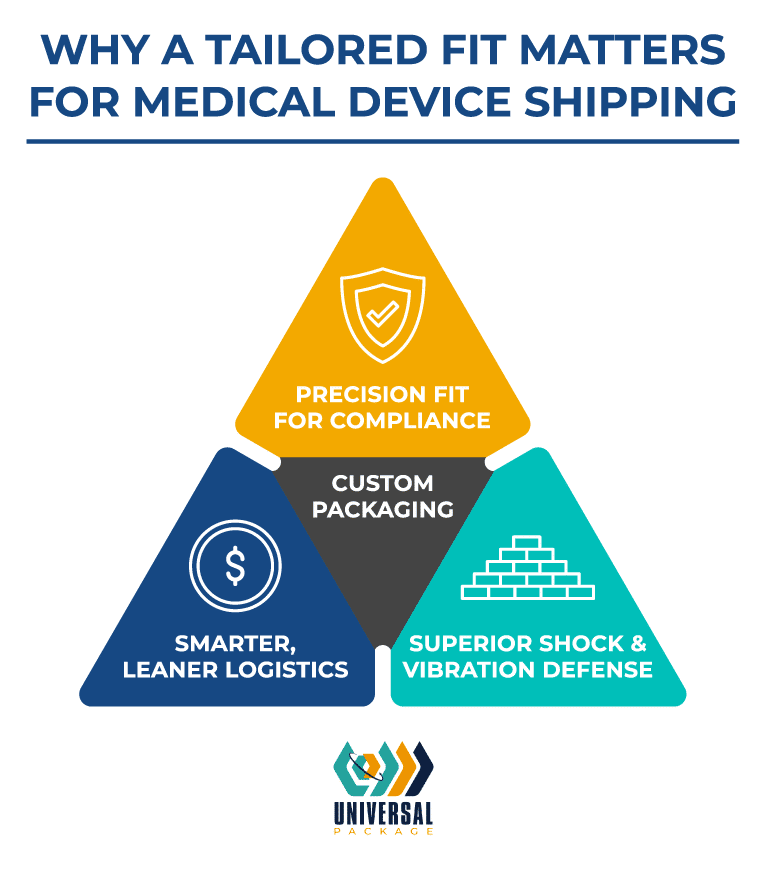
Custom packaging solutions address the specific needs of medical devices more effectively than standard options. Here’s how they offer distinct advantages:
Tailored Safety and Compliance
Custom packaging is designed to match the precise dimensions, weight, and fragility of each device. This exact fit can streamline sterilization processes and support regulatory compliance, potentially reducing the frequency of intensive revalidation efforts though not eliminating their need completely.
Optimized Logistics
By designing packaging to exact specifications, manufacturers can maximize space efficiency and decrease shipping costs. Innovative designs, such as collapsible sleeve packs and stackable totes, improve traceability and ensure that medical devices are securely stored during transit.
Enhanced Protection for Fragile Devices
For sensitive components like electronic instruments or precision devices, custom foam assemblies and tailored dunnage reduce movement and absorb shocks, ensuring robust protection throughout the supply chain.
Collaborative Design and Iterative Validation
Developing custom packaging solutions involves a collaborative process between manufacturers and packaging experts. This exchange of expertise supports compliance efforts and facilitates continuous improvement in design, testing, and validation protocols.
Best Practices for Ensuring Packaging Compliance
Achieving and maintaining compliance involves implementing a series of best practices:
Comprehensive Risk Assessments
Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential hazards at every stage of the packaging lifecycle. This process informs material and design choices while ensuring detailed documentation of compliance efforts.
Rigorous Testing and Validation
Implement real-world tests—such as vibration, drop, and compression evaluations—alongside accelerated aging studies to ensure packaging maintains its protective qualities. Regular revalidation guarantees that any changes to device specifications or sterilization methods do not compromise performance.
Early Integration of Storage and Transportation Requirements
Incorporate logistics considerations early in the design process. Insights from trial shipments and environmental analyses help select appropriate materials and design features that withstand varying transit and storage conditions.
Embedding Quality Management Processes
Foster ongoing compliance by integrating comprehensive quality management systems throughout packaging development. Continuous training and regular consultations with regulatory experts ensure that teams remain informed about the latest standards and best practices.
Documenting Compliance and Audit Preparedness
Meticulous documentation is essential for audit readiness and regulatory compliance. Detailed record-keeping of risk assessments, testing procedures, revalidation cycles, and design modifications not only bolsters a manufacturer’s defense against non-compliance issues but also simplifies the audit process. This systematic approach improves product traceability and supports ongoing efforts to enhance packaging quality.
The Digital Transformation of Packaging: From IoT to AI
The integration of digital tools is revolutionizing medical device packaging, transforming quality assurance and operational transparency. These emerging technologies work together to create a smarter, more resilient packaging ecosystem.
The Integration of IoT in Medical Packaging
Internet of Things (IoT) technologies now allow for active, real-time monitoring of packaging conditions during storage and transit. IoT-enabled sensors can track critical environmental factors, notifying manufacturers with immediate alerts if there are deviations from set conditions. This capability not only allows for immediate corrective action but also creates a verifiable digital record for regulatory audits and supports data-driven refinements in future packaging designs.
Advanced Technological Integration in Packaging Innovation
Building on this foundation of data, other advanced technologies are boosting functionality and compliance. Automation and robotics are being implemented to enhance the precision of packaging operations, significantly minimizing the risk of human error. Layered on top of this, Artificial Intelligence (AI) can monitor packaging integrity in real time, predict potential failures, and prompt preventative measures before a breach occurs. Furthermore, machine learning applications analyze production data to improve efficiency and accelerate turnaround times.
Together, these technological integrations create a powerful system for robust quality control, ensuring that packaging processes are not only compliant but also continuously improving through innovation.
Future-Proofing Your Packaging Strategy: Resilience, Collaboration, and Innovation

In a landscape shaped by technological advancements, shifting market demands, and global instability, a forward-looking packaging strategy is essential for success. Manufacturers must move beyond meeting today’s standards and actively prepare for the challenges of tomorrow by focusing on three key pillars: resilience, collaboration, and innovation.
Building Supply Chain Resilience
Global challenges, from geopolitical shifts to climate-related disruptions, demand flexibility. A future-proofed strategy involves designing adaptable packaging systems that can accommodate alternate materials or logistics partners on short notice. This includes engineering solutions that can handle unexpected environmental conditions and incorporating the flexibility to transition between reusable and disposable options based on current market needs and supply chain stability.
Driving Collaborative Innovation
The era of siloed development is over. In a rapidly evolving industry, collaboration is a key driver of progress. Leading manufacturers are forming strategic partnerships with research institutions, technology providers, and even competitors to share insights and co-develop solutions that meet ambitious safety and sustainability goals. These industry partnerships foster an invaluable exchange of knowledge, accelerating the adoption of cutting-edge materials and refining packaging designs to meet emerging regulatory and market demands.
Anticipating Future Trends and Technologies
The medical packaging industry will continue to evolve. Trends such as personalized packaging for patient-specific devices and the need for smaller, more flexible production batches are already emerging. To prepare, manufacturers are investing in research and development and embracing predictive analytics and advanced simulation tools. These technologies enable companies to foresee potential packaging failures, model the performance of new materials, and address challenges proactively, long before they can compromise product integrity or compliance.
By embedding resilience, fostering collaboration, and embracing innovation, manufacturers can build a robust packaging strategy that not only safeguards public health but also secures a competitive edge in a dynamic global market.
Workforce Empowerment and Training in Packaging Management
A knowledgeable workforce is indispensable for effective packaging management. Comprehensive training programs covering regulatory requirements, advanced packaging technologies, and quality management practices ensure that staff can implement and maintain compliant solutions.
Cross-training among quality control, logistics, and manufacturing departments further enhances efficiency and prepares teams to address regulatory updates. Regular workshops and certification programs, aligned with industry standards, empower employees and drive continuous improvement.
From Compliance to Competitive Edge: Your Strategic Partnership
In today’s fast-evolving regulatory landscape, prioritizing safety, durability, and compliance in medical device packaging basics is more critical than ever. Manufacturers can achieve these goals by leveraging custom packaging solutions, rigorous testing protocols, and cutting-edge technological integrations that ensure devices remain secure and compliant throughout their lifecycle.
Universal Package is ready to support your efforts with tailored, high-performance packaging solutions that deliver unparalleled safety, regulatory compliance, and resilience. Enhance your competitive edge—contact Universal Package today to discover how our innovative solutions can meet your critical medical packaging needs.